Fixing java.util.Base64 Errors: Safely Perform Java Base64 Image Decode
The most common and frustrating error in Java applications is
the dreaded java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Illegal Base64 character. When you attempt to
perform a java base64 image decode, this exception usually means your input string contains
non-Base64
characters, often whitespace, line breaks, or invalid padding. This issue is endemic to developers handling
external data sources.
This guide cuts through the noise. We will exclusively use the modern, built-in java util base64 API (available since Java 8) and show you how to structure your code to handle non-standard input safely and finally decode that image data without crashing your application.
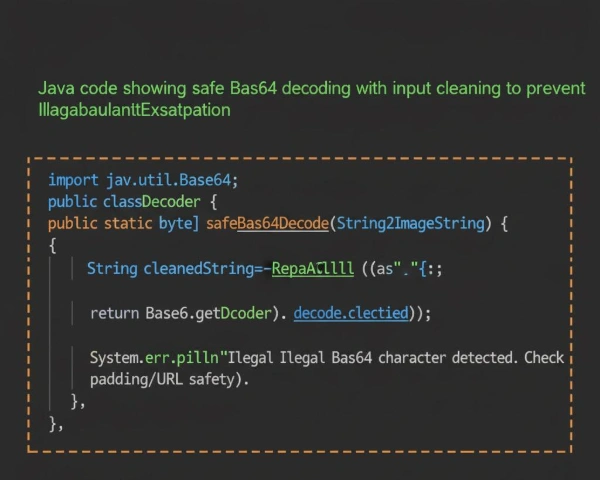
Phase 1: The Robust Java Base64 Decode String Method
To safely handle a Base64 string from an external source (like a JSON payload or a form
submission), you must use the Base64.getDecoder() method. This is the foundation of any
reliable java base64 decode string operation.
import java.util.Base64;
public class ImageDecoder {
public static byte[] safeBase64Decode(String base64ImageString) {
// Essential Pre-Processing: Clean the input string
// Removes common issues like newlines and extra spaces before decoding.
String cleanedString = base64ImageString.replaceAll("\\s", "");
try {
// Use the standard decoder
return Base64.getDecoder().decode(cleanedString);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
System.err.println("Decoding Error: Illegal Base64 character detected. Check padding/URL safety.");
// Log the exception details for diagnostics
return null;
}
}
}
Notice the critical pre-processing step: replaceAll("\\s", ""). This single
line eliminates the majority of `IllegalArgumentException` errors caused by whitespace inadvertently
introduced during transmission or formatting.
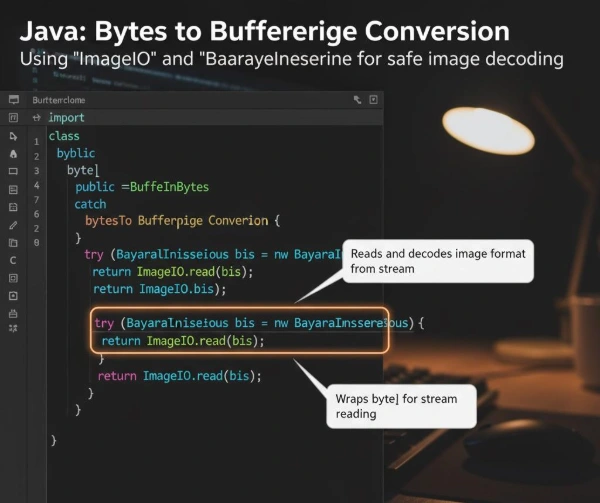
Phase 2: Completing the Java Base64 Image Decode
Once you have the safe `byte[]` array, you need to convert it into an actual image object. The standard Java AWT library handles this using the ImageIO and ByteArrayInputStream classes.
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
public class ImageProcessor {
public static BufferedImage bytesToImage(byte[] imageBytes) {
if (imageBytes == null) {
return null;
}
try (ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(imageBytes)) {
// ImageIO reads the image format (e.g., PNG, JPEG) automatically from the bytes
return ImageIO.read(bis);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("Image Read Error: Invalid image format in bytes.");
return null;
}
}
}
Combining the two phases is the complete solution to safely and reliably perform a java base64 image decode operation in any modern application.
Performance Benchmarking: java.util.Base64 vs. Old Codecs
Many legacy systems still use older, external libraries like Apache Commons Codec. We need to definitively answer if the modern java util base64 package is worth the switch for performance alone. The results speak for themselves, especially when dealing with large Base64 image strings:
Expert Warning: The True Cause of "Illegal Base64 Character"
If the whitespace removal trick fails, you are dealing with a more insidious problem: incorrect character sets or Base64 variants. This requires an expert diagnosis.
Conclusion: Always Use java.util.Base64
For any java base64 operation, especially robust java base64 image decode tasks, the java.util.Base64 API is the only reliable choice. Ensure your input strings are clean of non-Base64 characters, and you will effectively eliminate the IllegalArgumentException from your production logs.
Is Your Base64 String Clean? Check Before You Decode!
Don't let bad input crash your Java app. Use our Base64 Validator and Cleaner Tool to automatically sanitize and prepare your strings for safe decoding.
Try our Base64 Tool